31.3.2 STIs caused by viruses
HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, has been dealt with extensively in previous study sessions. Here we will focus on other STIs caused by viruses.
Herpes genitalis
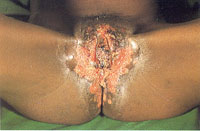
Herpes genitalis is the most common STI caused by a viral infection. The pathogen responsible for genital herpes is Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). Genital herpes usually presents with blisters that, when they break, lead to painful sores and ulcers in the outer surface of the genitals and in areas surrounding the anus. Following initial infection, it may take around 2–4 weeks for the lesions to heal, but symptoms usually recur weeks or months after the first outbreak. Although geneital herpes may affect anyone, if it involves an extensive area of the genitals and persists for longer than a month as seen in Figure 31.4, you should suspect an HIV-related opportunistic infection. Hence you should offer or refer these patients for provider-initiated HIV testing and counselling if their HIV status is unknown.
Genital warts
Genital warts is a viral STI caused by human papilloma virus (HPV) and commonly presents with small fleshy growths of skin on the genital area or around the anus (Figure 31.5). HPV has also been shown to be the causative agent of cervical cancer in women. However, the types of HPV that cause genital warts are not the same as the types that can cause cancer, which is usually asymptomatic for years.
Cancers (including cervical cancer) are covered in Study Session 3 of the Non-Communicable Diseases, Emergency Care and Mental Health Module.

31.3.1 STIs caused by bacteria
