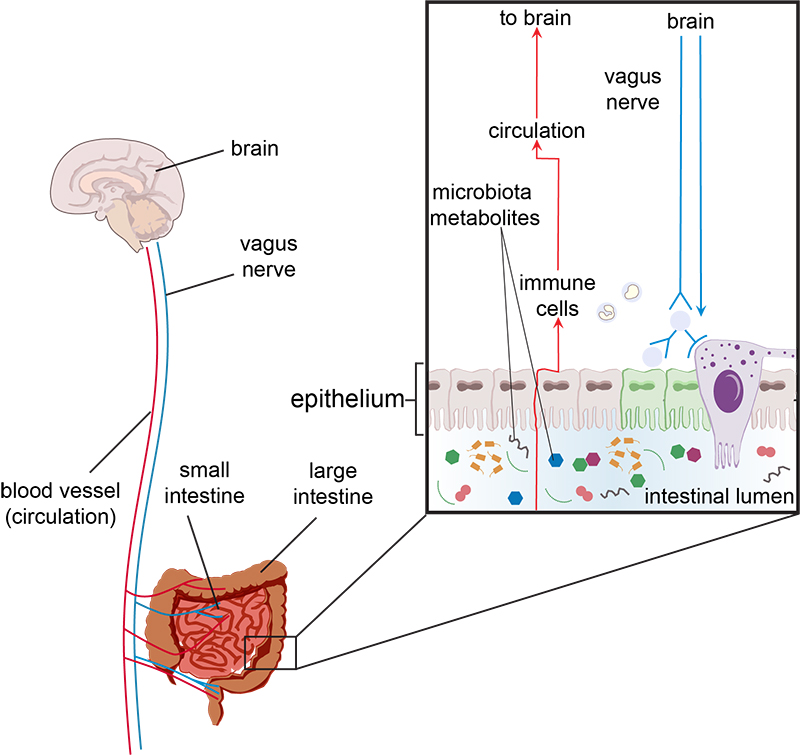
Figure 14 Microbiota gut-brain axis. Communication between the gut and brain is bidirectional. Metabolites produced by the microbiome are sensed by the intestinal cells, and this relays a signal via the vagus nerve to the brain. The metabolites can also be detected by immune cells which can directly stimulate the brain or stimulate the vagus nerve.
