6.2 Provision of goods such as education and healthcare
Access to education for all income levels enhances equality of opportunity. By undertaking training to learn new skills workers can improve their earning potential by adding to their human capital.
Those on low incomes might not be able to afford to undertake education or training, and so would not have the same opportunities as those on higher incomes. Therefore, provision of universal education by the government would allow greater opportunity for those on low incomes to increase their human capital.
Increased spending by the government on health services also benefits those on low incomes as improved healthcare enables workers to keep working.
Activity 14 Taxes and government spending
Figure 21 shows tax payments (below zero on the vertical axis) and benefits (above zero on the vertical axis) as a proportion of disposable income of households in different quintile groups in 2017.
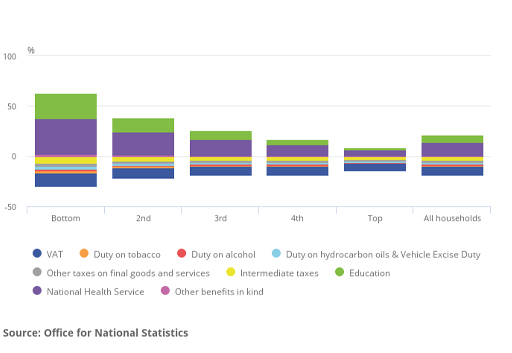
Which quintile group benefits the most from state provided education and the NHS?
Answer
The bottom quintile of the population receives in relative terms the highest benefit from education as shown by the green area in Figure 21. This becomes progressively smaller the higher the quintile group. The benefits of the NHS follow a similar pattern.
How do you think this affects inequality?
Answer
The lower quintiles benefit to a greater extent from state provided health and education. This would have the impact of reducing inequality as the standard of living of the lower quintiles are improved relatively more than the higher quintiles. This helps to produce more equal living standards across society.
