2.2.3 Medication: stimulant treatment
Recall that medication is an option for individuals of all ages with ADHD. For adults with the condition, medication is the first type of treatment recommended by NICE because evidence suggests that medication is more effective for this age group than other approaches. The first type of medication offered, irrespective of age group, is stimulant or psychostimulant drugs. These are a class of drugs that typically increase the activity of the central nervous system, which includes the brain.
These drugs were first discovered to be effective at reducing ADHD-like symptoms in the 1930s (Bradley, 1937), although the condition was not referred to as ADHD at that time. At low doses psychostimulants can, somewhat counter-intuitively given their name, reduce movement and impulsivity, while also improving cognitive function, including sustained attention and working memory (Solanto, 1998).
The psychostimulants used in the treatment of ADHD are amphetamine and methylphenidate. You may have heard of these under their respective well-known brand names of Adderall® and Ritalin®. Psychostimulants act to increase synaptic levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters.
-
Which neurotransmitters mentioned earlier in the course fall in the category of monoamines?
-
Dopamine, noradrenalin and serotonin.
Both drugs act on neurotransmitter transporter channels and have a larger effect on dopamine compared with the other two monoamines. They have an intermediate effect on noradrenalin and a relatively small impact on serotonin.
-
What is the role of the neurotransmitter transporter channel?
-
The transporter channel is normally responsible for removing neurotransmitter from the synapse.
The simplest action is by methylphenidate, which blocks the transporter (or reuptake) channel like a plug in a plug hole, preventing the neurotransmitter reuptake into the presynaptic neuron. This means the neurotransmitter stays in the synapse for longer and is more likely to bind with receptors. This is illustrated for methylphenidate in Video 7.
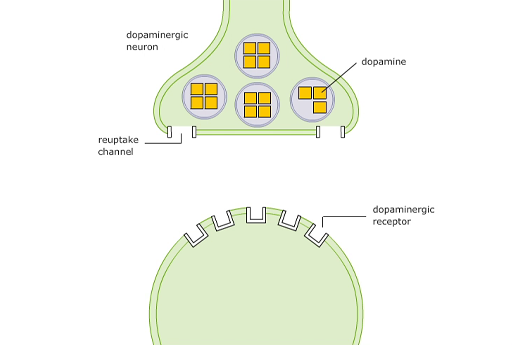
Transcript: Video 7 The actions of methylphenidate
Amphetamine is also able to block the transporter channel, but it has a second action as well, as illustrated in Video 8.
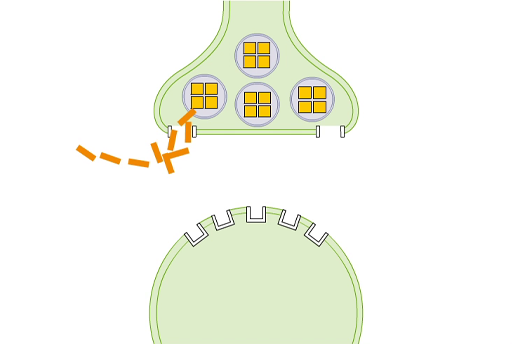
Transcript: Video 8 The actions of amphetamine
A high percentage of individuals with ADHD will see a reduction in their symptoms with methylphenidate (57%; Newcorn et al., 2008) or amphetamine (82%; Dittmann et al., 2013), as shown in Activity 9.
Activity 9 The impact of Ritalin
Watch Video 11 Ritalin/ Methylphenidate Review [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] [open this link in a new tab/window so you can easily return to this page after viewing the video] and answer the following questions.
Does the person in the video mention any side effects of Ritalin?
Discussion
Yes, he mentions appetite suppression, but he also mentions that Ritalin has fewer side effects than other drugs for ADHD.
What other problems does he mention with his experience on the drug?
Discussion
He mentions the ‘up and down’ nature of the effects, which means that it is hard to find the correct dose regime.
Does he feel the drug worked to relieve his ADHD symptoms?
Discussion
Yes, he mentions being able to focus more and being more engaged. For example, he felt able to read text books without being distracted. His reading comprehension also improved.
Despite the effectiveness of psychostimulant treatments for many, in some cases the side effects – which can range from insomnia to psychosis (Mariani and Levin, 2007) – cannot be tolerated, meaning individuals may stop taking the medication, or at least take it differently to how it is prescribed.
-
What are some other reasons why individuals might not take their medication as prescribed?
-
They may simply forget to take it, or they may not want to take it where others may see them, such as at school or at work, due to the stigma attached to taking medication or having ADHD.
This problem has been partly overcome by the development of long-acting versions of the drug which require fewer doses, meaning that individuals have to take it less often and may not need to take it during the school or working day. Treatment adherence, the extent to which a person takes their medication as recommended, is quite low for psychostimulants. A recent study found that adherence for psychostimulants over a 12-month period ranged from 5.4% to 28.4% in children and adolescents, and from 7.2% to 25.2% in adults (Setyawan et al., 2013). The range of values represents results from the use of different versions of the drugs, for example, longer-acting or shorter-acting versions (Setyawan et al., 2013).
Perhaps unsurprisingly based on these data, complete discontinuation of treatment is quite high for psychostimulant drugs, with 19% of individuals of all ages with ADHD discontinuing treatment with long-acting drugs and 38% discontinuing treatment with short-acting drugs (Lachaine et al., 2012). Various approaches are taken to support better compliance to medication, one of which is outlined in the box below.
Using an app to support treatment adherence
Researchers in Israel recently tested the research question of whether a mobile phone app could help support treatment adherence in children with ADHD (Weisman et al., 2017). They conducted a study with 39 boys and girls with ADHD, receiving psychostimulant medication, and their parents.
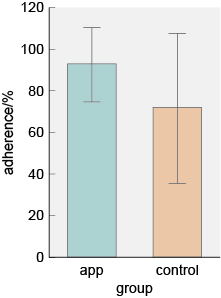
For around half of the participants, the parents downloaded and used an app for 8 weeks to remind them to give medication to their children. The remaining group, a control group, did not have any support. The researchers thought that those with the app would show different treatment adherence rates and they measured this by pill counts recorded daily by the parents, converted into a percentage of pills that should have been taken with full adherence to the treatment regime.
The results of the study are shown in Figure 14. After 8 weeks, participants in the group where parents received prompting by the app had statistically significantly higher treatment adherence rates.
-
Which of the two groups had the greatest variation around the mean? Explain your choice.
-
The control group had the greatest variation because the standard deviation (indicated by the length of the lines) is larger.
As well as difficulties with side effects and potential stigma, treatment with psychostimulants is not always acceptable to the individual or their parents because of their addictive properties.
However, individuals who do not get any benefit from psychostimulant treatment, or who choose not to take it for any reason, may respond to a non-stimulant medication.
