 free course icon
level 1: introductory icon
free course icon
level 1: introductory icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Introduction to differential equations
Differential equations are any equations that include derivatives and arise in many situations. This free course, Introduction to differential equations, considers three types of first-order differential equations. Section 1 introduces equations that can be solved by direct integration and section 2 the method of separation of variables. Section...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Life, Health and Chemical Sciences: PhD Projects 101
Ever wondered what our research students from the school of Life, Health and Chemical Sciences do in the labs? Check out these explainers of their projects...
 article icon
article icon
History & The Arts
Inventing the record business
As Spotify prepares to float itself, Eva Moreda Rodríguez hails their distant ancestors. Uncover the early years of the recording industry
 article icon
article icon
Health, Sports & Psychology
Science doesn't know how free divers do it
It's not a total mystery - but, explains Kevin Wong, there's still a lot about free diving that science can't quite explain.
 video icon
video icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Stephen Hawking in his own words
In this tribute created by the University of Cambridge, Stephen Hawking reflects on "a glorious time to be alive doing research"
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Stephen Hawking: A brief history of his timeline
Time travel might not be possible, but you can join us for a trip through Stephen Hawking's remarkable life.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Stephen Hawking: The tributes
Famous theoretical physicist, Professor Stephen Hawking had died aged 76. Here, academics from around the world pay tribute to the scientist...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
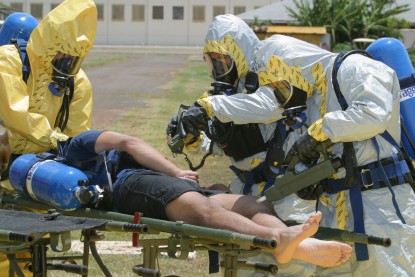
What are nerve agents - and what do they do?
It's a question the people of Salisbury weren't expecting to have to ask themselves following a quick trip to a Zizzi on a quiet Sunday. Sergei Skripal's apparent revenge poisoning, though, has brought chemical killers from the battlefield closer to home. Simon Cotton explains how they work.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
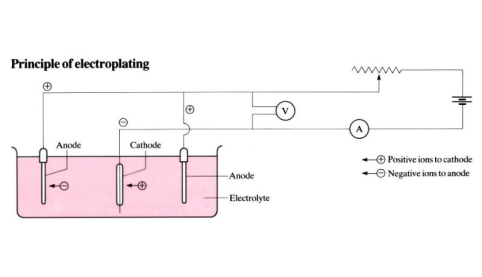
Electroplating
A process used to apply a coating, via electrolysis, from an electrically conductive base material to the object to be coated. Often used to silver plate cutlery and other decorative objects.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Shot blasting
Shot blasting entails the forceful direction of abrasive particles against the surfaces of metal parts to remove contaminants or condition the surface for subsequent finishing.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Shot peening
Shot peening is a method of cold working in which compressive stresses are induced in the exposed surface layers of metallic objects by controlled impingement of shot.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Nitrotec process (oxygen enhanced nitriding)
The Nitrotec process consists of nitriding (nitrocarburising) components, before immediately subjecting them to rapid oxidation, then quenching, finishing with the application of a protective sealant. Oxidation gives protection against corrosion, whilst the quenching and sealing give enhanced surface wear resistance and increased yield strength ...