 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
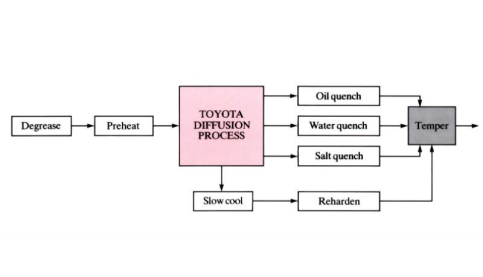
Toyota diffusion (TD)
Elements such as vanadium, niobium and chromium, are diffused into a ferrous metal component, via a chemical reaction that takes place in a high temperature salt bath with a borax mix. After quenching and tempering, a very hard carbide layer remains on the surface of the component. This surface coating is often applied to extend the life of ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
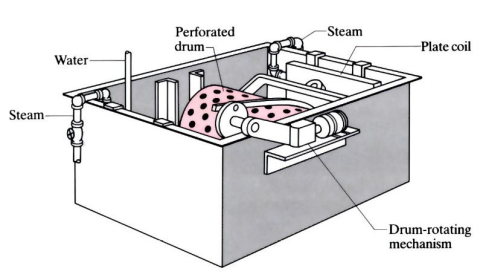
Phosphating (non-electrolytic coatings)
Often used on ferrous metals to provide a protective, corrosion-resistant phosphate film prior to painting. The phosphate coating, created via a precipitation reaction, adheres well to the base metal, also offering good surface adhesion for paint or powder coating.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
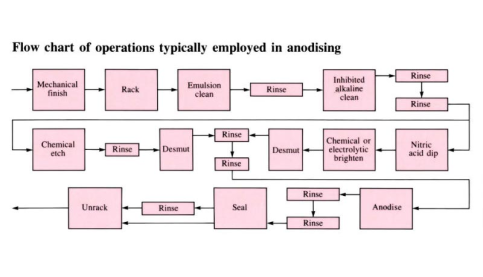
Anodising
An electrochemical process causes a layer of anodic oxide to form on the surface of a non-ferrous base metal, such as aluminium. Oxide provides protection from corrosion and wear, as well as a good surface finish for painting. Also used for decorative effect.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
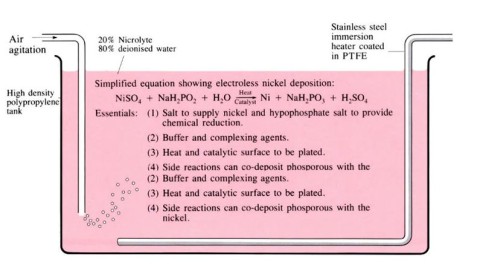
Electroless plating
Metal ions within a chemical solution, using an autocatalytic reaction, deposit a uniform layer onto the surface of prepared (cleaned and etched) material to be coated. The process is purely by chemical reduction and no electrical current is necessary.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
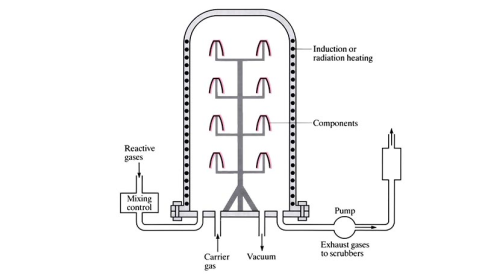
Chemical vapour deposition (CVD)
Reactive gases are fed into a heated chamber containing the component(s) to be coated. At elevated temperature, various gaseous phases chemically react with the heated surfaces of the component(s), and a solid, corrosion resistant coating is deposited onto those surfaces.
 article icon
article icon
Digital & Computing
From Zero Day to Doomsday – Public Lecture
We are delighted to invite you to From Zero Day to Doomsday, a lecture by Mike Richards on the WannaCry ransomware cyber-attack, which had serious implications last year for the NHS and businesses around the world.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
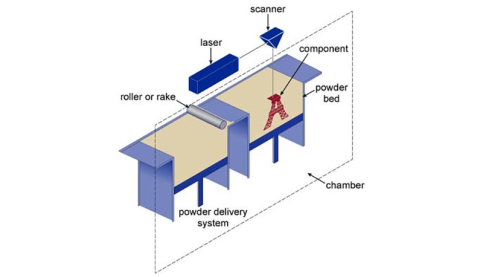
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Heat is generated using a focused heat source, normally a laser, sufficient to melt a thin layer of powder applied to the surface of a substrate. Material is added layer by layer by lowering the build by a small amount and spreading a thin layer of powder over the surface. To create the desired geometry, the heat source is traversed over the ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
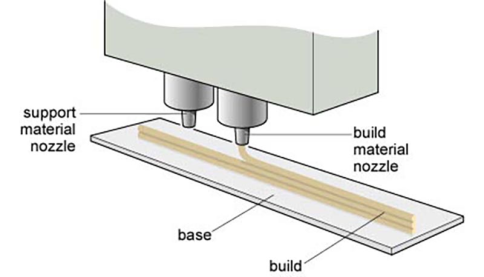
Fused deposition modelling (FDM)
Thermoplastics are heated to above their glass transition temperature and extruded onto a substrate to produce a raised track or filament. The desired geometry is created by manipulating the extrusion nozzle using a computer-controlled positioning system. Three-dimensional structures can be formed by adding material onto previously deposited ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
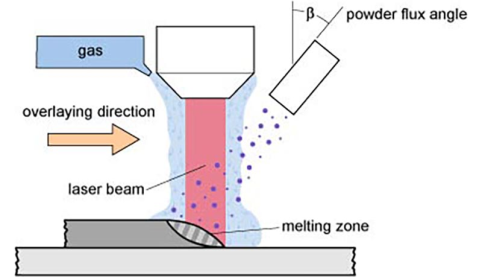
Direct metal deposition (DMD)
Heat is generated using a focused heat source of various kinds, sufficient to melt the surface of the substrate and form a small melt pool. Material is added to the melt pool using a focused powder stream or a wire feed system to form a raised portion of material. To create the desired geometry, the substrate is manipulated using a ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
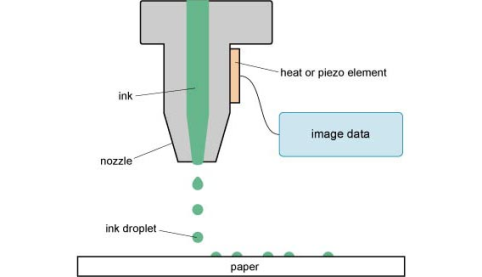
3D printing
Although often used as a blanket term for additive manufacturing, 3D printing is a technique where a print head is used to control the deposition of polymer on a substrate drop by drop.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
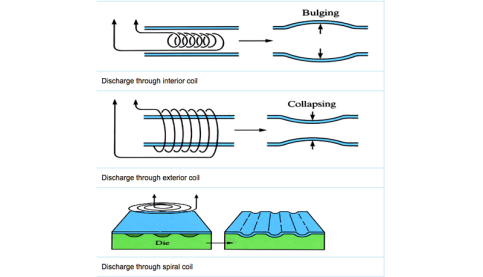
Magneform (electromagnetic assembly and forming)
A high energy rate, cold forming technique that reshapes metals without physical contact. When an electric current generates pulsed opposing magnetic fields near the metal, a controllable pressure is created.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
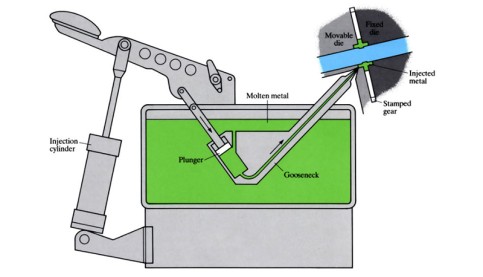
Injected metal assembly (Liquid riveting)
This refinement of die casting is a simple joining/assembly technique where components are accurately positioned and metal is injected into the cavity between the components and a die, solidifying almost instantaneously. The join, which may be stronger than the component itself, depends on the mechanical locking action and shrinkage of the ...