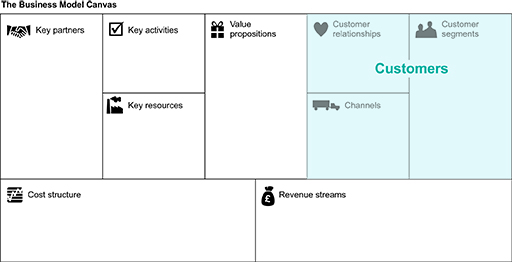
4.1.2 Customers area
Customers are shown in the customer area of the business model canvas. The customers area has three components: customer segments, customer relationships and channels. It is located in the right-hand corner of the business model canvas shown in Figure 3.
Customer segments
A customer segment is a group of customers having common characteristics (e.g. age, gender, location, lifestyle and interests). For instance, an organisation may choose to serve millennials as its customer segment.
A millennial is a person born between 1981 and 1996. Millennials rely on digital technologies, prefer personalisation in customer relationships, and expect to be attended via multiple customer channels (Davies, 2016).
Customer relationships
Customer relationships portray the type of relationship established with each customer segment. Osterwalder et al. (2010, p. 29) distinguish six types of customer relationships:
Personal assistance
A representative is accessible to the customer in person or through a media (e.g. by phone, online). The representative supports the customer during the process.

Dedicated personal assistance
The customer has a dedicated assistant, which is the typical situation of some wealth management services which provide a key account manager for the customer, or in some law firms where corporate clients refer to a lawyer who represents the law firm and is responsible for serving the client.

Self-service
There is no direct relationship between the company and its customer, so customers help themselves in the purchase. An example would be the use of vending machines.

Automated services
This mode of service combines self-service with customisation based on automatic profiling of the customer, who will then receive personalised information. In doing so, it tries to personalise the relationship with the customer. An example is the ordering process on Amazon, which profiles the customer’s product preferences and uses this information to propose complementary products. Similarly, Netflix records the preference of customers for particular genres (e.g. adventure, drama, sci-fi) and automatically proposes new movies and series that match with customer preferences.

Communities
Communities of customers can serve the purpose of exchanging knowledge among other clients or potential customers, answer questions and solve problems. They are also important for collecting valuable information on products and services. It is the typical situation of software development, where communities develop around a specific software.

Co-creation
Some services are co-created by customers. This means that customers participate in the design, development and/or production of a product or a service. This is what happens with YouTube, whose videos are uploaded by users of the popular platform. Similarly, TripAdvisor’s reviews are created by users.

Activity 8 Customer relations quiz
a.
when an organisation chooses to design, develop, and produce a product or a service together with customers
b.
when customers produce and sell a product independently
c.
when several companies produce a product or a service together
d.
when an organisation chooses not to involve customers
The correct answer is a.
a.
Congratulations. This is the correct answer. Co-creation is when customers participate in the design, development and/or production of a product or a service.
a.
True
b.
False
The correct answer is a.
a.
Correct. Communities of customers can serve the purpose of exchanging knowledge among other clients or potential customers, answer questions and solve problems. They are also important for collecting valuable information on products and services. It is the typical situation of software development, where communities develop around a specific software.
Channels
Channels are interfaces between the company and its customers. A channel combines activities, people and organisations to deliver a product or a service to customers.
This building block of the canvas tries to answer the question: How do businesses reach customers? Osterwalder et al. (2010, p. 27) defines five types of channels shown in Table 1. The channels may be combined.
| Control of the channel | Type of channel | Channel | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Own | Direct | Sales force | Some fashion houses have a factory outlet near their production facilities or in large commercial areas to sell directly to customers at discounted prices.  |
| Web sales | Direct Line sells its insurance policies online through its website.  |
||
| Indirect | Own stores | H&M sells clothes in its shops, providing customers with a basic assistance by its sale force.  |
|
| Partner | Partner stores | In some Hilton Hotels customers can find fast food and other partner stores.  The same happens for online, with the partnership between e-tailers and fashion brands, such as the partnership between Alibaba and Valentino (see this article for more information). |
|
| Wholesaler | Car manufacturers sell cars to dealers that work as their wholesalers.  |
Activity 9 Channels quiz
a.
True
b.
False
The correct answer is b.
b.
Congratulations. This is the correct answer. An organisation can use different channels in combination.
a.
True
b.
False
The correct answer is b.
b.
Congratulations. This is the correct answer. Sales force, web sales and own stores are examples of own channels.
Now you have looked into customer area of the business model canvas you will move onto the next area— the infrastructure area.