Unit 2: Identify
2.7 Different forms of harm – definitions and indicators
There are various forms of harm and abuse. Below we give a detailed list of the recognised forms of significant harm and abuse that can occur.
Main forms of harm:
- Physical abuse results in actual or potential physical harm from an interaction or lack of interaction.
- Emotional abuse includes the failure to provide a developmentally appropriate, supportive environment, including the availability of a primary attachment figure.
- Sexual abuse is the involvement of a child or vulnerable adult in sexual activity that he or she does not fully comprehend, is unable to give informed consent to, or for which the child or vulnerable adult is not developmentally prepared and cannot give consent, or that violates the laws or social taboos of society. Sex with a child by an aid worker is always sexual abuse, even if it looks like there may have been consent.
- Sexual or commercial exploitation includes using children or vulnerable adults to work or perform other activities for the benefit of others where the perpetrator profits monetarily, socially, politically, or in other ways where there is an exchange of gifts, cash, or in kind for sex.
- Neglect or negligent treatment is the inattention or omission on the part of the caregiver to provide for the development of the child or vulnerable adult in all spheres.
Other sub-types of abuse:
- Traditional harmful practices are practices based on cultural beliefs and values.
- Spiritual abuse is using text from spiritual books or quoting scripture as an excuse to perpetrate abuse and violence or to instil fear in children and vulnerable adults.
- Modern slavery includes the crimes of human trafficking, slavery, and slavery-like practices.
- Financial and material abuse includes theft, fraud, exploitation and pressure in connection to wills, property, inheritance and financial transactions.
- Domestic abuse or intimate partner violence is any incident or pattern of incidents of controlling, coercive, or threatening behaviour, violence, or abuse of adults.
The following forms of harm may happen in the workplace, but not exclusively:
- Discriminatory abuse exists when values, beliefs or culture result in a misuse of power that denies opportunities to some groups or individuals.
- Bullying is behaviour directed either against an individual or a group of individuals that creates a threatening or intimidating environment.
- Harassment means unwelcomed verbal, non-verbal or physical conduct that is related to a person’s characteristics, whether they are actual or perceived.
- Sexual harassment is any unwelcome sexual advance, request for sexual favour, verbal or physical conduct or gesture of a sexual nature, or any other behaviour of a sexual nature that might reasonably be expected or be perceived to cause offence or humiliation to another.
A fuller definition of each of the forms of harm and abuse summarised above is available in this PDF download.
![]()
Want to find out more?
For more detailed information on the terminology used in safeguarding, follow the link below:
Glossary of Terms developed by Bond
|
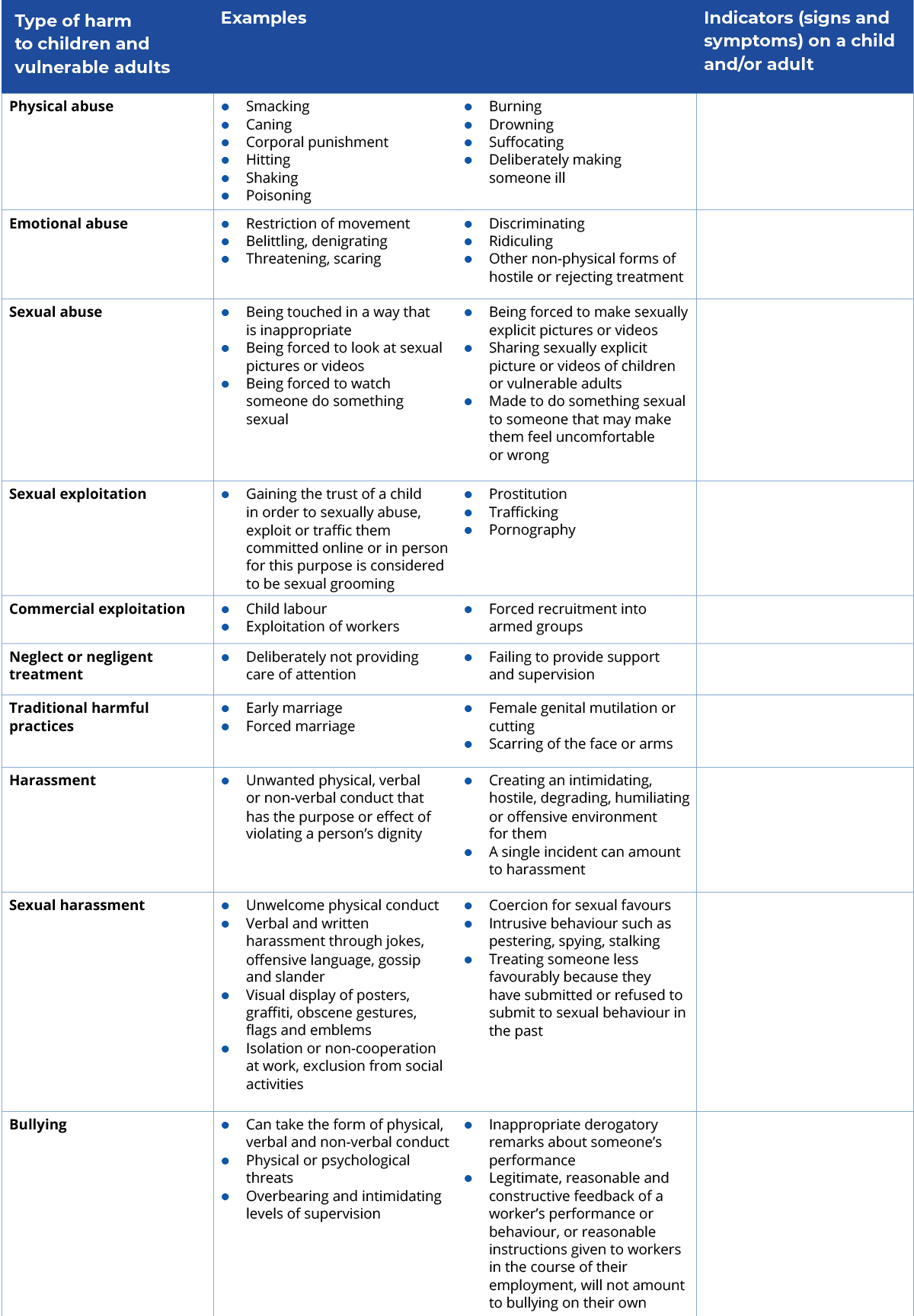
Activity 2.4 Types of harm In the table below, the first column lists the different types of harm you learnt about in the previous exercise. The second column details different examples for that particular harm. But what are the indicators of these different kinds of harm? In the third column of the table add as many indicators (signs and symptoms) as possible for each kind of harm. It might be helpful to discuss this more widely with staff and generate as many ideas as possible. Use this downloadable PDF version of this table to help you complete the table.
|