What is sustainability?
In the following video, Dr Richard Newton provides an introduction to sustainability concepts and principles, covering the first five sections of this unit.
Sustainability has many definitions from many sources, but everyone has heard of it and knows of its importance. The definition here is provided by the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the UN.
“the management and conservation of the natural resource base, and the orientation of technological and institutional change in such a manner as to ensure the attainment and continued satisfaction of human needs for present and future generations. Such sustainable development (in the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sectors) conserves land, water, plant and animal genetic resources, is environmentally non-degrading, technologically appropriate, economically viable and socially acceptable ”
In short, sustainability is defined as preserving the resource base and minimising damage to ecosystems, while maintaining the economic viability and human rights of populations in the present and for future generations.
Therefore, sustainability encompasses the long-term stability and viability of the environment, economy, and society. Increasingly it is also including the rights of animals and their welfare.

Figure 1: United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
The UN Sustainable Development Goals encompass an ambitious list of targets but there are many trade-offs and nuances especially regarding food production. As populations grow, there are ever-increasing demands to provide healthy and nutritious food in a responsible manner. This is further exacerbated by rising affluence, which leads to populations demanding a wider range of higher quality, more energy-intensive food choices. To fully understand the interactions of supply chains and their impacts, we need to look at “food systems” through a wide lens rather than focusing on the production unit alone. Food systems include all of the different interconnected businesses and sectors that interact along a food value chain as well as the policy framework and socio-economic conditions that drive food production.
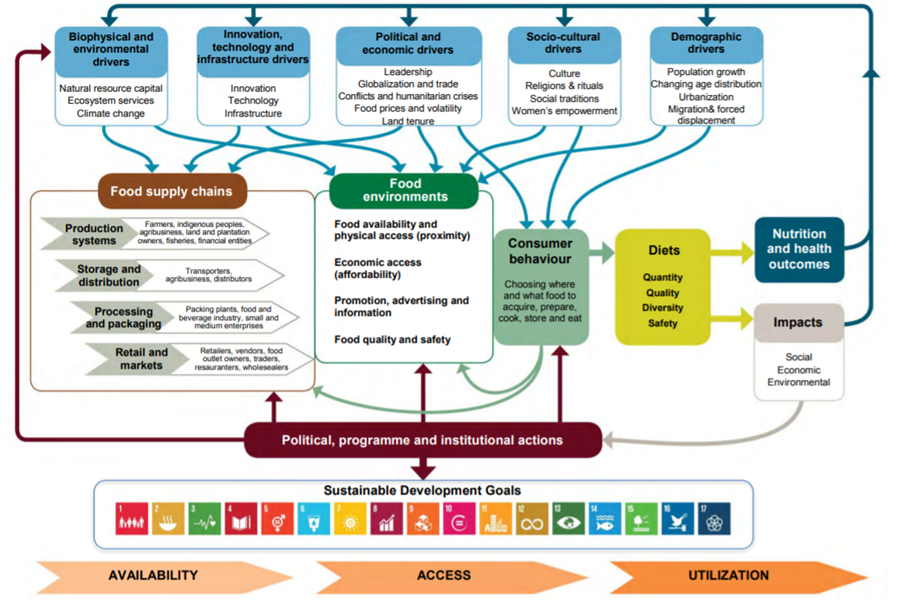
Figure 2. Conceptual framework of food systems. Source: HLPE. 2017. Nutrition and food systems. A report by the High-Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security, Rome.
