 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
What is Manupedia and how do I use it?
Find out more about Manupedia and how you can best make use of it.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
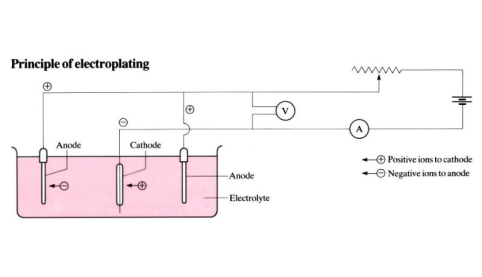
Electroplating
A process used to apply a coating, via electrolysis, from an electrically conductive base material to the object to be coated. Often used to silver plate cutlery and other decorative objects.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
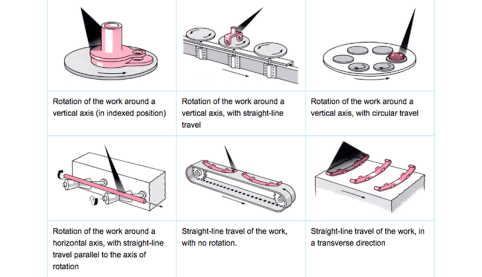
Shot blasting
Shot blasting entails the forceful direction of abrasive particles against the surfaces of metal parts to remove contaminants or condition the surface for subsequent finishing.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Shot peening
Shot peening is a method of cold working in which compressive stresses are induced in the exposed surface layers of metallic objects by controlled impingement of shot.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Nitrotec process (oxygen enhanced nitriding)
The Nitrotec process consists of nitriding (nitrocarburising) components, before immediately subjecting them to rapid oxidation, then quenching, finishing with the application of a protective sealant. Oxidation gives protection against corrosion, whilst the quenching and sealing give enhanced surface wear resistance and increased yield strength ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
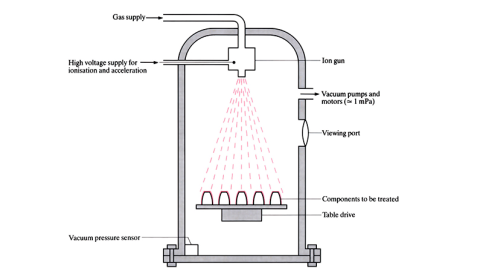
Ion implantation
Within a vacuum chamber, surfaces to be hardened are bombarded with a high energy stream of ions that penetrate the surface. This is not a diffusion process. Once impregnated into the surface, the ions (usually carbon or nitrogen) lose their energy and stop moving. The compressive stresses generated in the surface layers improve mechanical and ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Induction/flame hardening
Induction hardening involves using induced electrical currents to very rapidly generate heat via hysteresis, usually in a workpiece made from medium to high carbon steel. Flame hardening uses oxy-fuel burners to heat the workpiece via conduction. Both procedures use quenching after heating, often followed by tempering and/or stress relieving.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
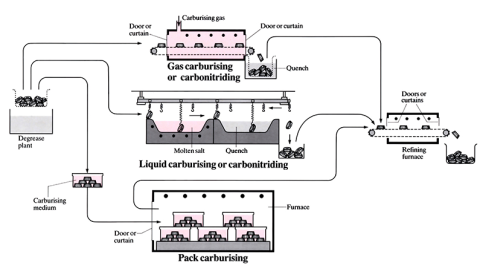
Carbonitriding / carburising
Carbon or carbon and nitrogen together, in a medium of gas, solid or liquid, are diffused into the surface of component(s), particularly those made from low carbon steels. Changes to the chemical composition of the surface (austenite) lead to high carbon content in the surface material, which when quenched transforms to a hard coating (martensite).
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
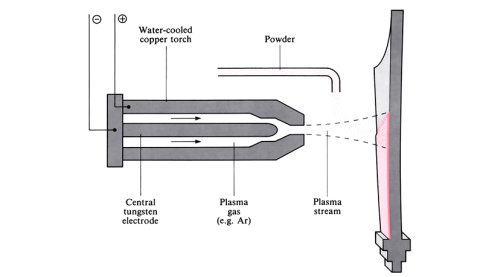
Plasma arc spraying
A stream of high temperature plasma and the powder coating material are carried via an electric arc, to the workpiece to be coated.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Plasma nitriding/carburising
The surface of the workpiece is saturated with either carbon atoms (carburising plasma) or nitrogen atoms (nitriding plasma). Carburising, carried out at high temperatures, involves bombarding the surface to be coated with the plasma. The workpiece is held under vacuum until carbon atoms have diffused into the heated surface, to form hardened ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
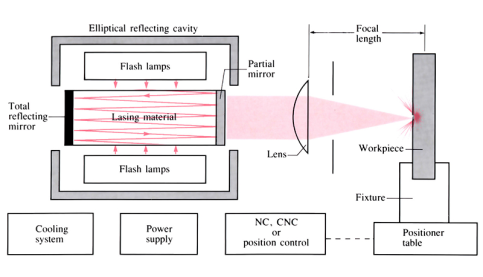
Laser surface treatment
A surface treatment used to harden or clad surfaces of ferrous metals. For hardening, a laser beam with a high power density heats a small area on the surface of the workpiece, causing changes to the atoms in the lattice of the material (austenite). As the beam moves away, to another spot on the surface, the heated area is rapidly cooled by the ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
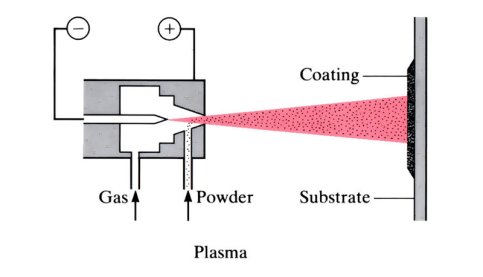
Thermal spraying (Hardfacing)
The surface to be coated is cleaned and roughened, to provide adhesion of molten particles in the coating material when it’s sprayed onto the workpiece. The coating material is melted using thermal, electrical or thermochemical means. Molten materials (metals, alloys or ceramics) are sprayed onto a substrate material (the component) where they ...
