 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
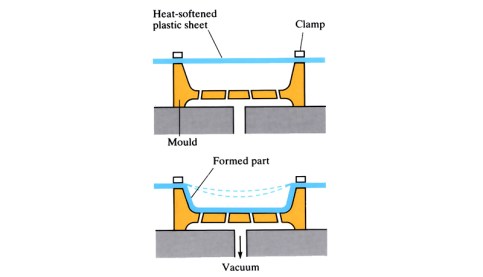
Vacuum Forming (Thermoforming)
A sheet of plastic, softened by heat, becomes pliable and when placed under vacuum adopts the shape of male or female mould.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Why do volcanoes erupt?
What forces create these geological timebombs?
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
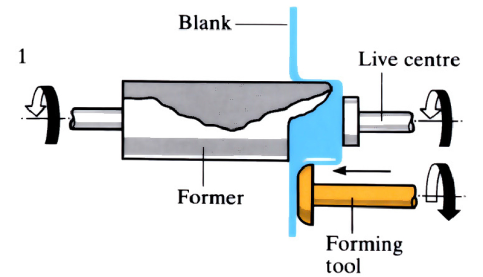
Metal Spinning / Flow Turning
Spinning is a process used to produce an axis-symmetric hollow shape by the application of lateral pressure from a forming tool, to a rapidly revolving circular blank of sheet material, causing it to assume the shape of a former that is rotating with it.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
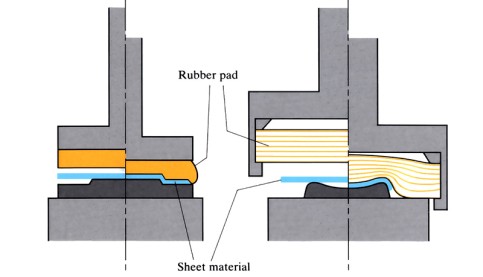
Fluid and Rubber Die Forming (Guerin and Hydroform)
Sheet metal is placed between a solid die and a rubber pad. Under pressure from a rigid tool, the rubber behaves like a liquid and forms over the shape of the die, forcing the sheet metal to also adopt the die shape.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Explore systems thinking with OpenLearn
Get to grips with systems thinking - dip into our wide range of resources here on OpenLearn
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
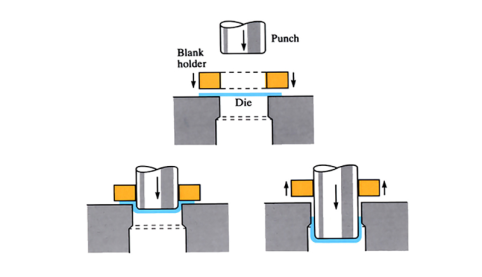
Deep Drawing
A sheet blank, subjected to a peripheral hold-down pressure, is forced by a punch into and through a die to form a deep recessed part, having a wall thickness substantially the same as that of the blank.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
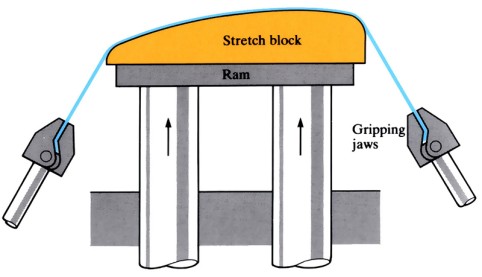
Stretch forming
Contoured, curved shapes are formed from sheet metal pressed, stretched and bent over a die. Typical applications include curved panels such as car door panels or wing panels on aircraft.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
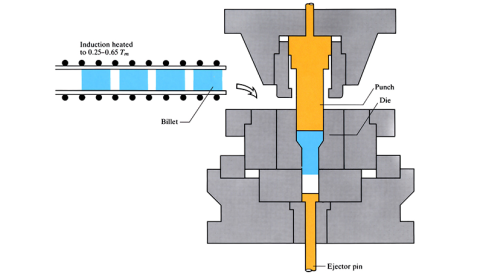
Warm forging
The workpiece billet is heated to temperatures between 0.25 and 0.6 Tm. A close fitting punch is used to exert pressure on the malleable metal billet held in a heated, closed die until forged to the required shape.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
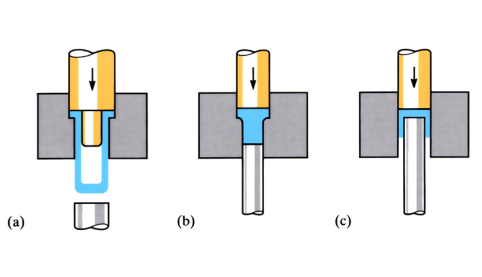
Cold forging
A forging process carried out at temperatures below 0.25Tm. A closely fitting punch is used to exert pressure on malleable metal held in the die.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
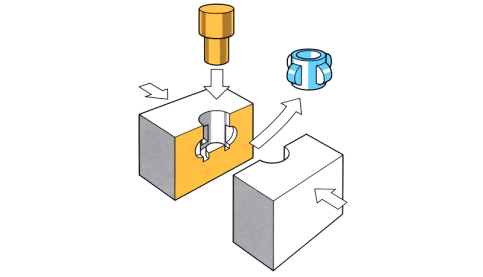
Axiforge process
Axiforge process can be carried out on dies, positioned on vertical or horizontal axes, within a press. Sideways ram movements apply pressure to the outside of a split die, so that the two parts close around a heated billet, forming it into the required external shape. This is followed by pressure from one or two piercing punch(es), which pierce...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
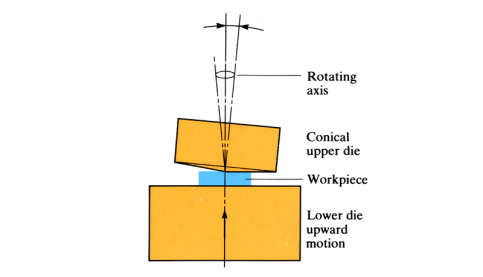
Orbital forging
Workpiece material is forged between two dies. The bottom die moves upwards whilst the top die, tilted to a preset angle, rotates (orbits) around the central axis, progressively forming the malleable material into the required shape.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
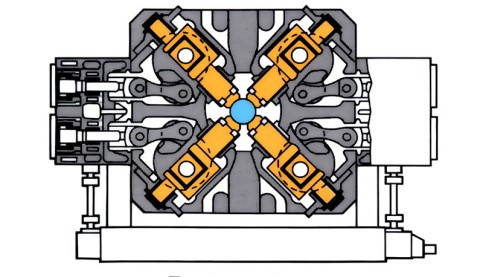
Rotary Forging, General Forging Machine (GFM) and Swaging
A circular housing contains a rotating shaft (rotor) holding free moving anvils. At the end of each anvil is a die. The dies surround a centrally placed workpiece. Revolving around the rotor is a cage holding loosely rotating rollers. As the cage rotates, the rollers impact on the anvils, which effectively hammer the stationary workpiece into ...