Summary of Section 2
- Nitrogen in the atmosphere is relatively inert due to its strong triple bond.
- Bacteria in the roots of plants fix nitrogen from the atmosphere.
- Industrially the Haber-Bosch process fixes nitrogen:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) = 2NH3(g)(Equation 8)
- Nitric acid is produced by the Ostwald process:
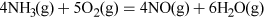 (Equation 11)
(Equation 11)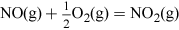 (Equation 12)
(Equation 12)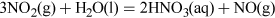 (Equation 13)
(Equation 13)Nitric acid is then used to make ammonium nitrate fertiliser.
- Excess levels of nitrate, NO3−, in water can result in eutrophication in the environment. While high levels of nitrate in drinking water are dangerous for infants because the nitrate can be reduced to nitrite in the body which may interfere with oxygen binding by haemoglobin.
- Arsenic levels in natural waters correspond to the oxoanions arsenite, AsO33-, and arsenate, AsO43-.
- Excess nitrate or arsenate can be removed from water by ion-exchange chromatography.
- Fluoride is important in dental health but if levels are too high in drinking water then health problems may result.
