What enzymes can be applied for proteolysis?
The enzymes that break the peptide bonds of fish protein leading to peptides, of different sizes, and even free amino acids are called protease (also known as peptidase or proteinase). They are hydrolytic enzymes and are globally classified into two groups: endopeptidase (breakdown of nonterminal amino acids) or exopeptidase (breakdown at the ends of the protein chain releasing amino acids). Another classification is based on the reactivity of the catalytic amino acid present on the protease, that is, aspartate protease, glutamate protease, metalloprotease, cysteine protease, serine protease, threonine protease, and asparagine protease (Figure 1).
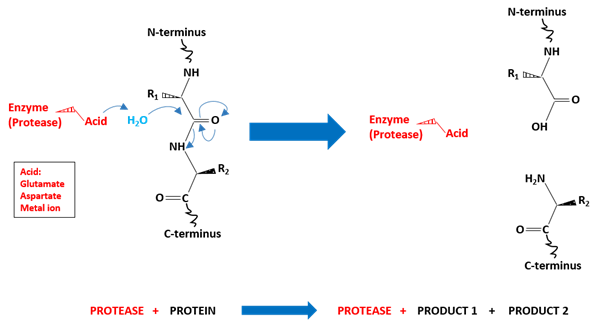
Figure 1. Catalysis mechanism of peptide bond breakdown by aspartate, glutamate or metalloproteases
The commercial name of proteases is established for different reasons such as, its origin, the substrate that specifically catalyses, or the optimal range of pH activity. Thus, some examples of these proteases are:
Papain is an endopeptidase (cysteine protease) isolated from papaya and is active in the range of pH (6-8) and T (40-80ºC).
Bromelain is an endopeptidase (cysteine protease) obtained from pineapple and is active in the range of pH (6-8) and T (30-60ºC).
Trypsin is an endopeptidase (serine protease) recovered from the digestive system of vertebrates and is active in the range of pH (6.5-9.5) and T (4-65ºC).
Pepsin is an endopeptidase (aspartate protease) isolated from the digestive system of vertebrates and is active in the range of pH (1.5-3.0) and T (30-45ºC).
Alcalase (subtilisin A) is an endopeptidase (serine protease) produced by Bacillus licheniformes with activity in the range of pH (6.5-9.0) and T (40-70ºC).
Carboxypeptidase A is an exopeptidase obtained from the pancreas with activity in the range of pH (7.0-10.0) and T (45-75ºC).
Aminopeptidase N is an exopeptidase recovered from the small intestine with activity in the range of pH (7.0-9.0) and T (30-60ºC).
Elastase (breaks elastin fibers), collagenase (breaks collagen molecules), protamex (non-bitter FPH), fluoryzyme, protease M, esperase, etc.
