Biochemical characterisation of collagen. Charge and hydrophobicity by HPLC
Different chromatography techniques could be employed for assessing several characteristics of collagen:
Ion exchange chromatography (iEX) is a very useful technique for the separation of charged molecules, such as proteins, differing by just one amino acid, based on ionic interactions. It gives information about the charge degree of different collagen components. Figure 11 shows the separated alpha-1 chain and the beta components of collagen extracted from fish skin by-products.
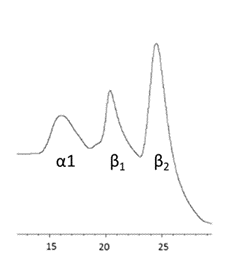
Figure 11. Fish collagen iEX-HPLC elution profile showing alpha 1 chain and beta components.
Reverse Phase chromatography (RP-HPLC) is used for the separation of molecules operating on the principles of hydrophobic interactions. The separation depends on the hydrophobic binding of the solute in the mobile phase to the immobilised hydrophobic ligands attached to the stationary phase. Different retention times indicate differences in hydrophobicity of collagen components (Figure 12).
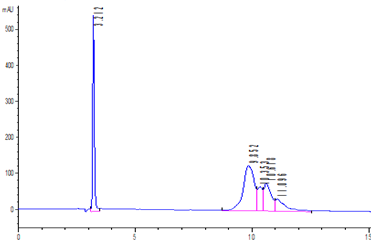
Figure 12. RP-HPLC of collagen from turbot aquaculture skin by-products.
