4.3.2 Propagation
Once a small number of chains have been started, propagation involves successive addition of monomer units to achieve chain growth. At each step the free radical is regenerated as it reacts with the double bond. So in the case of styrene the propagation step is
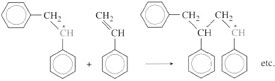
The free radical can also add on in a different way to produce
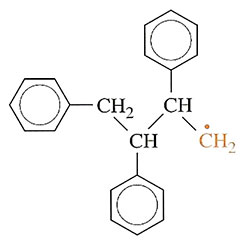
but this process happens only rarely since the free radical is less stable than in the first case.
The junction that is formed normally is known as a head-to-tail link while the abnormal link is head-to-head. The effect is limited to about 1 per cent of the total number of monomer links in normal polystyrene, but it is important because the head-to-head links are weaknesses in the chain. Since they are of higher energy, thermal degradation can start at these defective junctions.
